Looking to maximize your PPC campaign performance? Google Ads A/B testing is the answer you’ve been searching for. In this comprehensive guidebook, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about creating, implementing, and analyzing A/B tests to significantly improve your Google Ads performance.
Whether you’re struggling with low CTA (click-through rates) or want to boost your conversion metrics, understanding how to properly test your ads will give you the competitive margin your business needs in today’s digital landscape.
Introduction
Have you ever thought why some Google Ads campaigns perform brilliantly while others fall flat despite targeting the same audience? The secret often lies in strategic Google Ads A/B testing – a powerful methodology that removes guesswork from your advertising equation.
A/B testing in Google Ads is a systematic approach where you run two or more variations of an advertisement simultaneously to determine which version performs better. By testing different elements against each other, you get solid data about what relates to your target audience instead of depending on assumptions.
For businesses investing in pay-per-click advertising, A/B testing isn’t just helpful—it’s a must. Without testing, you’re essentially flying blind, actually wasting budget on underperforming ads while missing opportunities to connect with your audience.
In this guide to Google Ads A/B testing, we’ll explore everything from basic testing concepts to advanced strategies that can transform your campaign performance. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to implement effective ad split testing techniques that boost clicks, conversions, and your bottom line.
1. Understanding Google Ads A/B Testing
1.1 What Is A/B Testing in PPC?
Google Ads A/B testing is the practice of running two versions of an ad simultaneously with a single variable changed between them to determine which performs better. Think of it as a controlled experiment for your advertising.
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between testing methodologies:
- A/B testing: Tests two versions with one variable changed
- Split testing: Usually refers to testing completely different ad concepts
- Multivariate testing: Tests multiple variables simultaneously to see how they interact
For digital advertisers, the benefits of implementing Google Ads A/B testing are substantial:
- Remove subjective decision-making from your ad creation process
- Find out what messaging truly resonates with your target audience
- Gradually improve performance metrics like CTR, conversion rates, and ROAS
- Keep up with changing market conditions and what consumers want
1.2 How Google Ads A/B Testing Works
At its core, Google Ads A/B testing follows a controlled experiment methodology where you:
- Identify what element you want to test
- Create two versions: a control (your current ad) and a challenger (the variation)
- Split your audience randomly between versions
- Collect performance data over a statistically significant period
- Analyze results to determine a winner
It’s important to understand the distinction between true A/B testing and Google’s ad rotation feature. While ad rotation shows different ads within an ad group, proper A/B testing via Google Ads experiments gives you more control over traffic split, measurement parameters, and statistical significance.
Speaking of statistical significance, this concept refers to whether your results reflect actual performance differences rather than random chance. A confidence level of 95% or higher generally indicates that your test results are reliable and actionable.
2. Why Google Ads A/B Testing Matters for Business Growth
2.1 Benefits of A/B Testing in Google Ads Campaigns
Implementing regular Google Ads A/B testing delivers measurable benefits that directly impact your advertising ROI:
Increases click-through rate (CTR): By discovering which headlines, descriptions, and calls-to-action resonate best with your audience, you’ll naturally see improvements in how often users click your ads. Even small CTR improvements can significantly impact traffic volume over time.
Improves quality score: Google rewards relevant, high-performing ads with better quality scores. Better quality scores mean lower costs and better ad positions—a win-win scenario created through consistent PPC testing.
Lowers cost-per-click (CPC): As your ads become more relevant and generate higher CTRs, you’ll often see your cost-per-click decrease. This efficiency allows you to either reduce spend while maintaining results or increase your reach without increasing budget.
Boosts conversions and ROAS: Perhaps most importantly, well-tested ads drive more conversions at a lower cost, improving your return on ad spend. One client saw a 32% conversion rate improvement after just three months of structured ad variations testing.
2.2 Impact on User Experience and Ad Relevance
Beyond pure performance metrics, Google Ads A/B testing significantly enhances the user experience. When you deliver ads that precisely match searcher intent, users find what they’re looking for faster, making them more likely to engage with your business.
Through testing, you’ll discover which messaging best aligns with:
- Different stages of the buyer journey
- Various audience segments’ specific pain points
- Diverse user motivations and preferences
This improved relevance creates a positive feedback loop where users have better experiences, Google rewards your ads with better positions and lower costs, and your business benefits from higher-quality traffic.
3. What Elements Should You A/B Test in Google Ads
3.1 Ad Copy Elements
The most common starting point for Google Ads A/B testing is your ad copy:
Headlines: Test different approaches like question-based headlines versus statement headlines, benefit-focused versus problem-focused, or including numbers versus not including them. Your headline tests often deliver the most dramatic CTR improvements since they’re the most prominent ad element.
Descriptions: Experiment with variations in your value proposition, feature-benefit combinations, urgency statements, and proof points. Small description tweaks can significantly impact conversion rates even when CTRs remain similar.
CTAs (Call-to-Action): Test direct commands (“Buy Now,” “Sign Up Today”) against softer approaches (“Learn More,” “See Options”) to discover what motivates your specific audience to click and convert.
3.2 Visual and Asset Elements
For campaign types that include visual components, these elements deserve equal attention in your ad split testing strategy:
Images: Test different styles (lifestyle vs. product-focused), color schemes, perspectives, and subject matter. Image testing is particularly crucial for Display, Performance Max, and Shopping campaigns.
Logos, video creatives: Experiment with logo placement, video length, opening sequences, and messaging approaches to identify what captures and maintains audience attention.
3.3 Audience and Targeting
Google Ads A/B testing extends beyond creative elements to include who sees your ads:
Demographics, location, device targeting: Test performance differences between age groups, geographic regions, or users on different devices to refine your targeting strategy.
Custom intent audiences: Compare performance between audiences based on different intent signals to discover which potential customers are most valuable to your business.
3.4 Landing Pages
Your testing strategy should extend beyond the ad itself to destination pages:
Headlines, layout, CTA buttons, forms: Test variations in how you present information, arrange page elements, and request user information. Landing page Google Ads A/B testing often reveals surprising insights about what drives conversions after the click.
3.5 Ad Extensions
This additional information snippets deserve testing attention:
Sitelinks, callouts, structured snippets: Experiment with different extension combinations, wording, and ordering to maximize the real estate your ad occupies and provide users with the most compelling additional information.
3.6 Bidding Strategies and Budgets
Even your behind-the-scenes settings need to be tested:
Manual vs. automated bidding: Compare performance between different bidding strategies to find the right balance between control and optimization.
Impression share vs. conversion focus: Test whether prioritizing visibility or efficiency delivers better overall results for your specific business objectives.
4. Methods for Running A/B Tests in Google Ads
4.1 Using Google Ads Experiments
The most robust method for Google Ads A/B testing is through the platform’s built-in Experiments tab:
The Experiments feature allows you to:
- Create controlled tests with precise traffic splitting
- Compare performance metrics side-by-side
- Measure statistical significance automatically
- Implement winning variations with a single click
Google Ads offers several experiment types, including:
- Custom Experiments: Test virtually any campaign element
- Asset Experiments: Focus specifically on creative elements
When setting up experiments, proper traffic splitting is crucial. For most tests, a 50/50 split provides the fastest path to statistical significance while ensuring fair comparison.
4.2 Manual A/B Testing in Google Ads
If you prefer more hands-on control, manual PPC testing approaches include:
Setting up duplicate campaigns or ad groups: Create identical structures with one changed variable, then alternate between active periods or split your budget evenly.
Using labels and schedules: Tag different ad variations for easy tracking and schedule them to run during comparable time periods.
Manual Google Ads A/B testing provides flexibility but has downsides, such as inconsistent sample sizes and challenges in isolating variables. It also demands careful documentation and analysis.
4.3 Using Google Ads Variations Tool
For quick ad copy testing, the Ad Variations tool provides efficiency:
This feature lets you:
- Find & Replace: Swap specific words or phrases across multiple ads
- Swap Headlines: Test different headline positions and combinations
- Update Text: Make systematic changes across your account
While not as comprehensive as full experiments, the Variations tool excels at testing specific copy elements at scale across campaigns.
4.4 Third-Party Tools for PPC Testing
Several specialized tools can enhance your Google Ads A/B testing capabilities:
Optmyzr, Adalysis: Provide advanced analysis capabilities beyond native Google tools, Google Optimize: Ideal for in-depth landing page testing
External tools prove particularly valuable when:
- Testing across multiple platforms simultaneously
- Requiring more advanced statistical analysis
- Handling many accounts with several tests happening at the same time.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Google Ads A/B Testing
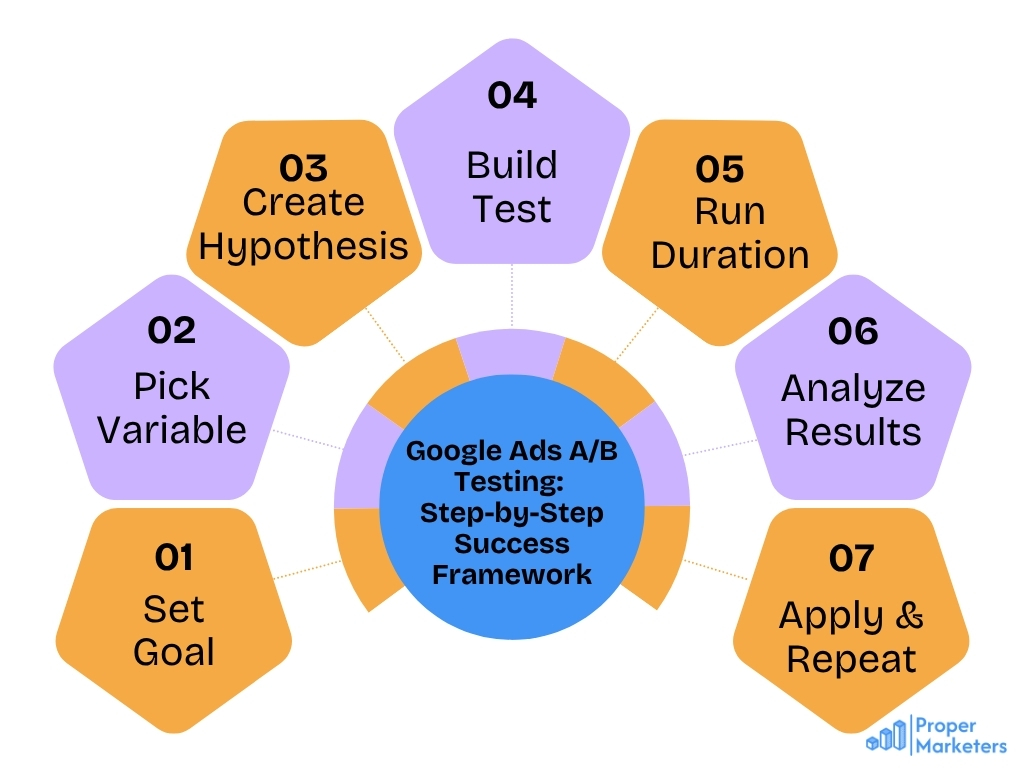
5.1 Define Your Testing Goal
Every successful Google Ads A/B testing initiative starts with a clear mark. Common testing goals include:
- Increasing click-through rate for awareness campaigns
- Reducing cost-per-acquisition for conversion-focused campaigns
- Testing new messaging approaches for specific audience segments
Your goal determines which metrics matter most and how you’ll evaluate success.
5.2 Choose One Variable to Test
The cardinal rule of effective A/B testing: change only one element at a time.
Testing multiple variables simultaneously makes it impossible to determine which change affected performance. By isolating a single variable—whether it’s a headline approach, a CTA phrase, or an image style—you gain clean, actionable insights you can build upon.
5.3 Create Hypothesis and Variation
Formulate a clear hypothesis before creating your variation. For example: “We believe that adding a 20% discount offer to the headline will increase CTR compared to our feature-focused control headline.”
A strong hypothesis:
- Identifies the specific change being tested
- Predicts the expected outcome
- Can be clearly proven or disproven by data
5.4 Set Up the Test in Google Ads
When configuring your Google Ads A/B testing experiment:
- Create a draft of your existing campaign
- Make only your single intended change
- Navigate to the Experiments tab
- Set traffic split (usually 50/50)
- Define success metrics aligned with your goal
- Set a duration that ensures sufficient data
Proper setup ensures valid results you can act upon with confidence.
5.5 Run the Test for a Meaningful Duration
Patience is vital for profound Google Ads A/B testing. Your test should run until:
- You’ve collected at least 1,000 impressions per variation
- You’ve recorded at least 100 clicks per variation
- The test has run through a complete business cycle (typically 2-4 weeks)
- You’ve reached statistical significance (95 %+ confidence)
Cutting tests short leads to unreliable conclusions and potentially costly mistakes.
5.6 Analyze the Results
Focus your analysis on metrics that directly connect to your initial goal:
- CTR for awareness and traffic goals
- Conversion rate and CPA for acquisition goals
- ROAS for revenue-focused objectives
Statistical significance tells you whether differences between variations reflect genuine performance differences rather than random fluctuations. Most Google Ads experiments aim for 95% confidence before declaring a winner.
5.7 Implement Winning Variation and Iterate
Once you’ve identified a winner:
- Apply the winning variation
- Document what you learned
- Develop a new hypothesis based on this insight
- Begin your next test
Successful Google Ads A/B testing is cyclical—each test informs the next as you continually refine performance.
6. Best Practices and Critical Thinking for Effective A/B Testing
6.1 Best Practices to Follow
Maximize the value of your Google Ads A/B testing efforts by following these proven principles:
Avoid testing too many things at once: Maintain experimental integrity by changing just one variable per test.
Use a sufficient sample size: Small data sets produce unreliable results. Continue tests until you have statistically significant data.
Don’t end tests prematurely: Resist the urge to declare winners before reaching statistical significance, even if early results seem dramatic.
Use consistent messaging across ad and landing page: Ensure your testing maintains alignment between what users see in the ad and what they experience after clicking.
6.2 Critical Thinking Tips for Better PPC Testing
Develop a more sophisticated testing approach by:
Avoiding false positives: Question unusually dramatic results and verify them with follow-up testing.
Validating assumptions with data: Let metrics challenge your preconceptions about what messaging will vibe with your audience.
Knowing when results are inconclusive: Sometimes tests show that both variations perform similarly. This itself is a valuable insight that can shape your strategy.
7. Advanced A/B Testing Tactics
7.1 A/B Testing in Google Display Campaigns
Display ad variations require special consideration:
Image formats: Try different sizes, angles, and placements to see which ones grab attention the best.
Placement targeting: Compare performance across different website categories and specific placements to refine your targeting strategy.
Visual elements often outweigh copy in importance for Display campaigns, making image-focused Google Ads A/B testing particularly valuable.
7.2 A/B Testing for Performance Max Campaigns
For Performance Max, focus your ad split testing on:
Asset groups: Test different combinations of headlines, descriptions, and images to identify the most favourable groupings.
Messaging variations: Experiment with how you communicate benefits and offers within the constraints of this automation-heavy campaign type.
Best practices for using image assets: Test image style, subject matter, and composition to discover what drives performance across multiple placements.
7.3 A/B Testing for Google Shopping Ads
Shopping campaigns benefit from testing:
Product titles: Experiment with different formats, feature highlights, and benefit statements in your product feeds.
Descriptions: Test which product details and selling points drive higher CTR and conversion rates.
Images: Compare different angles, backgrounds, and presentation styles to identify what helps products stand out.
7.4 A/B Testing Across Multiple Campaign Types
Create cohesive experiences by:
Aligning messaging in Search, Display, Shopping, Video: Test consistent themes across formats to discover what resonates universally versus what needs channel-specific adaptation.
Coordinated Google Ads A/B testing across campaign types reveals deeper insights about your audience’s preferences throughout their journey.
8. Interpreting & Acting on Test Results
8.1 Evaluating Performance Metrics
Develop a holistic approach to result analysis by considering:
CTR, CVR, CPC, ROAS, impression share: Look beyond primary metrics to understand the full performance picture.
Segmenting results by audience/device: Sometimes, overall results hide important insights about specific segments. A test might show no overall winner but reveal that mobile users strongly prefer one variation while desktop users prefer another.
8.2 Common Mistakes in Reading Results
Avoid these interpretation pitfalls:
Misjudging statistical significance: Remember that confidence level matters. A 10% improvement with 70% confidence isn’t reliable enough to base decisions on.
Ignoring external factors: Always consider whether seasonality, competition, news events, or other external factors might be influencing your test results.
8.3 How to Document and Apply Learnings
Maximize the long-term value of your Google Ads A/B testing:
Creating internal knowledge bases or test libraries: Document every test, hypothesis, and outcome to build organizational knowledge over time.
Use case: Consider how one client discovered through ad variations testing that highlighting their 24/7 availability outperformed messaging about their 20-year experience. This single insight led to a complete campaign overhaul that increased conversions by 43%.
9. FAQs About Google Ads A/B Testing
Q1. How long should a Google Ads A/B test run?
Ans: Most tests require 2-4 weeks to gather sufficient data for statistical significance. Low-traffic campaigns may need longer, while high-volume campaigns sometimes reach conclusive results faster.
Q2. What budget should I allocate for testing?
Ans: Dedicate 10-15% of your total Google Ads budget to ongoing testing initiatives. This investment typically pays for itself many times over through improved performance.
Q3. Should I A/B test a campaign that’s already working?
Ans: Absolutely. Even high-performing campaigns have room for improvement, and market conditions constantly change. Never stop testing, even with your best performers.
Q4. How often should I run A/B tests?
Ans: Ideally, you should always have at least one active test running. Once you implement a winning variation, immediately begin testing the next element or hypothesis.
Q5. What if the results are too close to call?
Ans: When variations perform similarly, this indicates that the element you’re testing isn’t significantly impacting performance. Move on to test something else that might have a greater impact.
10. Conclusion
Google Ads A/B testing isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s an important practice for any business to determine about maximize their digital advertising ROI. Through systematic PPC testing, you eliminate guesswork, discover what really connect with your audience, and continuously improve performance metrics that directly impact your bottom line.
Successful advertisers know that testing is not just a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. Each Google Ads experiment helps refine what you have learned before, creating a cumulative effect. This process sets you apart from competitors who rely on guesses instead of data.
Ready to transform your Google Ads performance through strategic ad split testing? Our team of Google Ads specialists can implement advanced testing methodologies customized to your specific business goals. We’ll handle the technical setup, data analysis, and performance optimization as you focus on growing your business.
Contact us today to discuss how our data-driven Google Ads management services can help you in achieving breakthrough results through systematic A/B testing and continuous optimization.
