In today’s digital landscape, businesses need effective online advertising strategies to stand out among competitors and reach potential customers. When it comes to driving instant traffic and measurable results, few platforms match the power and precision of Google Search Ads. As the leading digital advertising platform, Google Search Ads offers unparalleled opportunities to connect with prospects exect time when they’re searching for products or services like yours.
But how exactly do Google Search Ads work? How can you harness their full potential without wasting your marketing budget? And what strategies separate successful campaigns from ineffective ones?
Whether you’re new to digital advertising or looking to enhance your existing Google Ads Search Campaign efforts, this all-in- guide will walk you through everything you need to know about creating, optimizing, and scaling Google Search Ads that deliver real business results.
What is Google Ads and Why It Matters
The Evolution of Google Ads
Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords until 2018) has come a long way since its launch in October 2000. What began as a simple text-based advertising system has evolved into a sophisticated marketing platform that powers businesses of all sizes worldwide.
In its early days, Google AdWords operated on a cost-per-impression model with just 350 advertisers. Today, Google Ads serves millions of advertisers and generates over $200 billion in annual revenue for Google, accounting for the majority of Alphabet’s total revenue.
How Google Search Ads Work
At its core, Google Ads functions as an auction system, but with a twist – it’s not just about who bids the highest. When someone searches on Google, the ad system conducts a lightning-fast auction to determine which Google Search Ads appear and in what order.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- When a customer enters a search query, Google scans its ad inventory for advertisers bidding on keywords related to that search.
- The system evaluates all eligible ads based on several factors:
- Your bid amount (how much you’re willing to pay for a click)
- Your ad quality score (relevance, expected click-through rate, landing page experience)
- Ad rank thresholds (minimum quality requirements)
- The context of the search (location, device, time of day, etc.)
- Google then determines which ads appear and their position on the page.
- You only pay when someone clicks on your ad (hence the term pay-per-click or PPC)
This auction happens billions of times per day, for every search query entered on Google.
Key Advantages for Businesses
Google Search Ads offer several distinct advantages over other advertising channels:
- Intent-based targeting: Unlike social media, where you’re interrupting users’ browsing experience, Search Network Ads reach people actively searching for solutions you offer
- Measurable ROI: Track every impression, click, and conversion with precise attribution
- Scalability: Start with an undersized budget and scale up as you identify what works
- Speed to market: Launch campaigns and start generating traffic within hours
- Granular control: Adjust targeting, messaging, and bidding at a highly detailed level
- Remarkable reach: Access to billions of daily searches across Google’s search network
Who Should Use Google Search Ads?
While practically any business can benefit from Google Search Ads, they’re particularly effective for:
- Local businesses seeking customers in specific geographic areas
- E-commerce stores wanting to promote specific products
- B2B companies targeting professionals searching for business solutions
- Service providers looking for leads and appointments
- Startups need to build brand awareness quickly
Whether you have $10 or $10,000 to spend daily, Google’s ad platform can accommodate your budget and business goals.
Types of Google Ads Campaigns Explained
While this guide focuses primarily on Google Search Ads, understanding the full ecosystem of Google’s advertising options will help you develop more integrated marketing strategies.
Search Ads
Google Ads Search Campaigns display text ads on search engine results pages during users’ search for particular keywords or phrases. These are the most common types of PPC Search Ads and what most people think of when referring to Google Ads.
Search ads typically consist of headlines, descriptions, display URLs, and potential ad extensions. They appear at the top and bottom of search results, marked with an “Ad” label.
Display Ads
Display campaigns show visual banner ads across Google’s Display Network, which covers around two million websites, videos, and apps. These ads are good for building brand awareness and remarketing to past website visitors.
Video Ads
Video campaigns run on YouTube and across the Google Video Partners network. These can range from skippable in-stream ads to bumper ads and video discovery ads.
Shopping Ads
For e-commerce businesses, shopping campaigns directly showcase product images and prices, and store information in search results. These product listings require a Google Merchant Center account linked to your Google Ads account.
Performance Max Campaigns
Introduced in 2021, Performance Max campaigns use automation and machine learning to show your ads across all Google channels from a single campaign. They optimize for your specific conversion goals using assets you provide.
App Campaigns
Designed for mobile app promotion, these campaigns help drive app installs or in-app actions across Google’s entire network, including Search, Play Store, YouTube, and the Display Network.
Smart Campaigns
Created specifically for small businesses with limited time and marketing expertise, Smart campaigns automate much of the campaign management process while still delivering targeted ads across Google properties.
When to Choose Search Ads
Google Search Ads are particularly effective when:
- You want to capture high-intent traffic from users actively searching for solutions
- You need immediate visibility and quick results
- You have specific keywords relevant to your business offerings
- You’re focusing on direct response and conversions rather than brand awareness
- You want a highly measurable campaign performance
Preparing for Your First Google Ads Campaign
Success with Google Search Ads begins long before you create your first campaign. Proper preparation will help you avoid wasted spending and achieve better results faster.
Defining Advertising Goals
Start by defining what you want to accomplish with your advertising. Common objectives include:
- Increasing sales of specific products or services
- Generating leads for the sales department to follow up
- Driving website traffic to build your audience
- Building brand awareness in your target market
- Promoting special offers or events
Your goals will affect every aspect of your campaign setup, from keyword selection to ad copy and bidding strategy.
Understanding Your Audience and Intent
Effective Google Ads Search Campaigns require a deep analysis of targeted audience and their search intent. Consider:
- What specific problems are they trying to solve?
- What language and terminology do they use in searches?
- Where are they in the buying journey? (researching, comparing, ready to purchase)
- What might trigger them to search for your offerings?
Search intent generally falls into three categories:
- Informational: Users seeking information or answers (“how to improve website speed”)
- Navigational: Users looking for a definite website or page (“Amazon customer service”)
- Transactional: Users ready to enclose a purchase or complete an action (“buy wireless headphones”)
Mapping your keywords and ad messaging to these intent types will significantly improve your campaign performance.
Keyword Research and Selection Strategy
Keywords are the base of successful Google Search Ads. Your research should identify:
- Short-tail keywords: Broader terms which have higher search volumes but are usually less specific in intent.t (“running shoes”)
- Long-tail keywords: More specific phrases with lower volume but higher conversion potential (“women’s waterproof trail running shoes size 8”)
- Competitor keywords: Terms related to competing brands (when appropriate and within trademark guidelines)
- Negative keywords: Terms you don’t want your ads to show for (to prevent wasted spend)
Effective keyword tools include:
- Google Keyword Planner (free with Google Ads account)
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- Moz Keyword Explorer
When building your initial keyword list, focus on relevance over volume. It’s better to attract 100 highly qualified visitors than 1,000 loosely interested ones.
Setting a Realistic Budget and Expectations
One of the most common questions about Google Search Ads is: “How much should I spend?” While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, consider these guidelines:
- Start with a test budget that allows for statistically significant data (typically at least $300-500 per month for small businesses)
- Calculate your target cost-per-acquisition based on customer lifetime value
- Recognize that some industries have much higher costs-per-click than others
- Plan for a learning period where performance will improve over time
As for expectations, understand that immediate success is possible but not guaranteed. Most campaigns require 2-4 weeks of data collection and optimization before reaching optimal performance.
Account Structure: Campaigns, Ad Groups, and Ads
A well-organized account structure is crucial for effective management and optimization. Follow these best practices:
- Campaigns: Group by major themes, product lines, or business goals
- Ad Groups: Cluster tightly related keywords (10-20 max per ad group)
- Ads: Create at least three variations per ad group to test different messaging
For example, a furniture retailer might structure their account like this:
- Campaign: Living Room Furniture
- Ad Group: Sofas
- Ad Group: Coffee Tables
- Ad Group: TV Stands
- Campaign: Bedroom Furniture
- Ad Group: Beds
- Ad Group: Dressers
- Ad Group: Nightstands
This organized structure makes it easier to create relevant ads, track performance, and make targeted optimizations.
Writing Google Search Ads That Convert
The success of your Google Search Ads heavily depends on your ad copy. Even with perfect keyword selection and bidding, weak ad copy will result in poor performance.
Components of a Successful Ad
Standard Text Ads in Google Search have several key components:
- Headlines: Up to 3 headlines of 30 characters each
- Descriptions: Up to 2 descriptions of 90 characters each
- Display URL: The URL displays in your ad, which can include two path fields
- Final URL: The actual landing page users visit after clicking
Each element plays a decisive role in capturing attention and driving clicks.
How to Write Ad Copy Based on User Intent
Match your ad messaging to the user’s search intent:
- For informational queries, emphasize educational content and expertise
- For navigational queries, highlight your brand and make it clear that users will find what they’re looking for
- For transactional queries, focus on offers, pricing, and calls-to-action
For example, if someone searches “best CRM for small business”:
- Weak headline: “CRM Software Available”
- Strong headline: “Small Business CRM: Compare Top Features & Pricing”
Value Proposition and Differentiation
With limited character space, clearly communicate what makes your offering unique:
- Emphasize specific benefits rather than generic features
- Highlight unique selling points that competitors don’t offer
- Include credentials that build trust (years in business, awards, etc.)
- Mention guarantees or risk-reducers that make choosing you safer
For example:
- Weak: “Professional Plumbing Services”
- Strong: “24/7 Emergency Plumbers | 30-Min Response | No Weekend Fees”
Using Urgency and Emotional Triggers
Strategic use of psychology can significantly boost click-through rates:
- Create urgency with limited-time offers or seasonal messaging
- Appeal to emotion by addressing pain points or desired outcomes
- Use powerful words that trigger psychological responses
- Ask questions that engage curiosity
For example:
- Weak: “Weight Loss Program Available”
- Strong: “Lose 15+ Pounds By Summer? Our 60-Day Program (Spots Limited)”
Examples of High-Performing Ad Copy
Example 1: Local Service Business
- 24/7 Emergency Plumbers | [City]
- 15-Minute Response Guaranteed
- Licensed Experts, No Callout Fees.
- Free Quote & Same-Day Service Available.
Example 2: E-Commerce
- 70% Off Designer Watches | Sale Ends Tonight
- Authentic Luxury Watches With Certificate
- Free Overnight Shipping & 2-Year Warranty.
Example 3: B2B Software
- Cloud Accounting Software For Small Business
- Reduce Bookkeeping Time By 75%. Free 30-Day Trial.
- 5-Star Rated By 10,000+ Small Businesses.
Landing Page Optimization for Google Ads
Your advertising journey doesn’t end when someone clicks your ad—it’s just beginning. The landing page experience is a must for converting that click into a customer.
Why Landing Page Quality Impacts Your Ad Performance
Google evaluates landing page quality as part of your overall Quality Score. Poor landing pages lead to:
- Higher cost-per-click
- Lower ad positions
- Wasted ad spend as visitors bounce without converting
More importantly, even the best Google Search Ads won’t generate conversions if they send traffic to an ineffective landing page.
Key Elements of a High-Converting Landing Page
The most successful landing pages typically include:
- A clear, compelling headline that matches the ad’s promise
- A concise copy that expands on the benefits mentioned in the ad
- Strong visual elements (images, videos) that support the message
- Trust indicators (testimonials, reviews, security badges)
- A single, prominent call-to-action
- Minimal navigation to maintain focus on conversion
- Mobile-friendly design that works on all devices
Speed, Mobile Responsiveness, and Relevance
Technical performance significantly impacts conversion rates:
- Page speed: Visitors abandon pages that take more than 3 seconds to load
- Mobile optimization: Over 60% of searches now come from mobile devices
- Relevance: The page content must directly relate to the ad and search query
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Mobile-Friendly Test tools to identify improvement opportunities.
Message Match Between Ad and Page
“Message match” refers to the uniformity between your ad and landing page. When someone clicks an ad promising “50% Off Organic Dog Food,” the landing page should feature:
- A headline mentioning the same 50% discount
- Visual emphasis on organic dog food products
- The exact offer mentioned in the ad is readily available
Strong message match reduces visitor confusion and dramatically improve conversion rates.
A/B Testing and Continuous Improvement
Landing page optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly test variables like:
- Headlines and subheadings
- Image selection and placement
- Form length and fields
- Call-to-action wording and design
- Page layout and content structure
Even small improvements can significantly impact your conversion rates and ROI from Google Search Ads.
Understanding Google Ads Quality Score
Quality Score is one of the most important yet often misunderstood aspects of Google Search Ads performance.
Quality Score and Calculation
Quality Score is Google’s rating of the relevance and quality of your keywords, ads, and landing pages on a scale from 1-10. It’s calculated based on:
- Expected click-through rate (CTR): How likely users are to click your ad
- Ad relevance: How much your ad matches the intention behind a user’s search
- Landing page experience: The relevance and convenience of the landing page(lead capture page) is to the users who click on your ad
Quality Score is measured at the keyword level and is visible in your Google Ads account.
Importance of CTR, Ad Relevance, and Landing Page Experience
Why does Quality Score matter? Because it impacts:
- Ad position: Higher-quality ads achieve better positions
- Cost-per-click (CPC): Higher-quality ads pay less per click
- Ad eligibility: Low-quality ads may not show at all
In fact, improving your quality score from 5 to 8 could reduce your CPC by up to 50%, effectively doubling your advertising reach without increasing your budget.
How Quality Score Impacts Cost-Per-Click and Ad Ranking
Google determines ad rank using this formula:
Ad Rank = Bid × Quality Score (simplified version)
This means an advertiser with an excellent Quality Score can outrank competitors who bid higher but have poorer quality ads. For example:
- Advertiser A: $2 bid × Quality Score 9 = Ad Rank 18
- Advertiser B: $4 bid × Quality Score 4 = Ad Rank 16
Despite bidding less, Advertiser A would appear in a higher position due to a superior Quality Score.
Strategies to Improve Your Quality Score
To boost your Quality Score:
- Improve ad relevance: Create tightly themed ad groups with specific keywords and matching ad copy
- Enhance CTR: Write compelling ads that stand out and include keywords in headlines
- Optimize landing pages: Ensure they’re fast, mobile-friendly, and directly relevant to the ad
- Use ad extensions: Sitelinks, callouts, and structured snippets improve ad visibility and relevance
- Refine keyword selection: Remove poor-performing keywords and add negative keywords
A systematic approach to improving these factors can transform campaign performance while reducing costs.
Google Ads Targeting and Bidding Strategies
Beyond keywords and ad copy, sophisticated targeting and bidding options give advertisers precise control over who sees their ads and how much they pay.
Keyword Match Types
Google offers several keyword match types that control how closely a user’s search must match your keywords:
- Broad match: Reaches the widest audience but includes searches loosely related to your keyword
- Example: “women’s hats” could trigger ads for “ladies’ caps” or “female headwear”
- Phrase match: Triggers ads when searches include your keyword phrase or close variations
- For example, “tennis shoes” could match “men’s tennis shoes,” but not “shoes for tennis.”
- Exact match: Shows ads only for searches that match your keyword exactly or have the same meaning
- Example: [luxury hotel] would match “luxury hotels” but not “luxury resort hotels”
- Negative match: Block your ads from displaying for specific terms
- Example: “-cheap” would prevent your ad from showing for “cheap luxury hotels.”
For most advertisers, a mix of match types delivers the dynamic balance between reach and relevance.
Audience Targeting
While keywords target based on what people are searching for, audience targeting focuses on who is doing the searching:
- Demographics: Age, gender, parental status, household income
- Affinity audiences: People’s interests, habits, and lifestyles
- In-market audiences: People actively researching or planning purchases
- Remarketing: Previous visitors to your website
- Customer match: Targeting based on your own customer data
Combining keyword and audience targeting creates powerful opportunities for personalization and bid adjustments.
Geo-targeting and Device Targeting
Control where and on what devices your ads appear:
- Location targeting: Show ads only in specific countries, regions, cities, or even a radius around specific points
- Location bid adjustments: Increase or decrease bids based on geographic performance
- Device targeting: Customize campaigns for mobile, desktop, and tablet users
- Ad scheduling: Specify days and times when your ads should appear
These controls help allocate budget to the highest-performing segments of your audience.
Manual vs Automated Bidding
Google offers two primary approaches to bidding:
Manual bidding gives you direct control over maximum cost-per-click (CPC) bids for keywords or placements. This approach works well when:
- You have limited conversion data
- You want full control over specific keywords
- You have expertise in bid management
Automated bidding uses machine learning to set up bids based on the chance of achieving your goals. Options include:
- Maximize Clicks: Get as much clicks as possible within your budget
- Target CPA: Sets bids to achieve your target cost per acquisition
- Target ROAS: Aims for specific return on ad spend
- Maximize Conversions: Get as many conversions as possible within budget
- Enhanced CPC: Adjusts manual bids to increase conversion likelihood
For most advertisers, starting with manual bidding and transitioning to automated strategies as conversion data accumulates provides the best results.
Conversion Tracking and Analytics
Without proper tracking, you’re flying blind with your Google Search Ads campaigns. Implementing robust measurement is essential for optimization.
Why Conversion Tracking is Essential
Conversion tracking allows you to:
- Identify which keywords, ads, and campaigns generate leads or sales
- Calculate your true cost per acquisition across different segments
- Make data-driven decisions about budget allocation
- Prove the ROI of your advertising efforts
- Feed valuable data into automated bidding systems
Without conversion tracking, you can only optimize for clicks, not actual business results.
Setting Up Google Ads Conversion Tracking
Google offers several methods for tracking conversions:
- Website actions: Track form submissions, purchases, or other valuable user activities
- Phone calls: Monitor calls generated from your ads or website
- App installs or in-app actions: Track mobile app conversions
- Import: Bring conversion data from other systems like Google Analytics or CRMs
Basic website conversion tracking involves:
- Creating a conversion action in Google Ads
- Integrating the global site tag into your website
- Adding event snippets for specific conversion actions
- Testing to ensure data is being recorded properly
Connecting with Google Analytics and Tag Manager
While Google Ads provides conversion data, connecting with Google Analytics offers deeper insights:
- User behavior before and after clicking ads
- Multi-channel attribution models
- Site engagement metrics beyond conversions
- Enhanced demographic and interest reporting
Google Tag Manager simplifies implementation by:
- Centralizing all tracking tags in one interface
- Enabling non-technical team members to manage tags
- Facilitating A/B testing and advanced tracking scenarios
- Improving website performance through efficient tag loading
Metrics: CTR, CPC, CPA, Conversion Rate, ROAS
Key performance indicators for Google Search Ads include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Percentage of engagements that result in clicks
- Formula: (Clicks ÷ Impressions) × 100
- Benchmark: Varies by industry, but typically 1-5% for Search Network
- Cost Per Click (CPC): Average amount paid for each click
- Formula: Total Cost ÷ Total Clicks
- Benchmark: Varies widely by industry and keyword competitiveness
- Conversion Rate (CR): Percentage of clicks that end with conversions
- Formula: (Conversions ÷ Clicks) × 100
- Benchmark: Typically 2-10% for Search campaigns
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): Average cost to generate one conversion
- Formula: Total Cost ÷ Total Conversions
- Goal: Should be less than the customer lifetime value
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Revenue generated per dollar spent
- Formula: (Revenue ÷ Ad Spend) × 100
- Goal: Industry-dependent, but typically aiming for 200-400%+
Using Data to Improve Performance
Regular analysis should inform your optimization efforts:
- Weekly: Check basic metrics and make small adjustments
- Monthly: Conduct deeper analysis and make larger strategic changes
- Quarterly: Assess overall performance against business goals
Look for patterns such as:
- Keywords with high impression share but low CTR (ad relevance issue)
- Keywords with high CTR but low conversion rate (landing page issue)
- Time periods or locations with outsized performance (opportunity for bid adjustments)
- Devices with significant performance differences (opportunity for specific optimizations)
Let data guide your decision-making rather than assumptions or preferences.
Advanced Tactics to Maximize Results
Once you’ve mastered the fundamentals of Google Search Ads, these advanced techniques can help you gain a competitive edge.
Dynamic Search Ads
Dynamic Search Ads (DSA) automatically generate headlines and landing page destinations based on the content of your website. They’re excellent for:
- Catching long-tail keywords you might have missed
- Keeping ads updated with your website content
- Filling gaps in your keyword-based campaigns
To use DSA effectively:
- Start with a focused page feed or website section
- Write compelling description lines (Google only creates the headlines)
- Use negative keywords to prevent irrelevant matches
- Monitor search terms reports closely
Ad Extensions
Ad extensions expand your ads with additional information and links, improving visibility and click-through rates. Key types include:
- Sitelink Extensions: Additional links to specific pages
- Callout Extensions: Brief feature or benefit statements
- Structured Snippets: Lists of products, services, or features
- Call Extensions: Phone numbers for click-to-call functionality
- Location Extensions: Business address and map information
- Price Extensions: Showcase products or services with prices
- Lead Form Extensions: Allow users to submit contact information directly from the ad
Using all relevant extension types can increase CTR by 10-15% on average.
Responsive Search Ads
Responsive Search Ads (RSAs) let you create ads that adapt to show the most effective combinations of headlines and descriptions. Benefits include:
- Testing multiple headline/description combinations automatically
- Adapting ad copy to match more search queries
- Improving ad relevance across different devices and contexts
For effective RSAs:
- Provide at least 8-10 unique headlines and 3-4 descriptions
- Include a good mix of keyword-focused and benefit-focused headlines
- Pin certain headlines or descriptions to specific positions when necessary
- Review combination reports to identify top-performing elements
Remarketing Strategies
Remarketing allows you to rejoin with people who have previously interacted with your website. For Google Search Ads, consider:
- RLSA (Remarketing Lists for Search Ads): Tailor bids and ads for past visitors when they search on Google
- Customer Match: Upload customer lists to target existing customers with special offers
- Similar Audiences: Target new users with behaviors similar to your converters
Effective remarketing segments include:
- Cart abandoners
- Product viewers who didn’t purchase
- Past customers are due for repurchase
- Blog readers who haven’t converted
Lookalike Audience Building
Similar audiences (Google’s version of lookalikes) help you find new prospects who share characteristics with your best customers. To leverage this feature:
- Create a seed audience of your highest-value customers
- Apply similar audiences to your search campaigns
- Monitor performance and adjust bids accordingly
- Refine your seed audience based on results
Ad Scheduling and Dayparting
Ad scheduling allows you to show ads only during specific days and times, or adjust bids during high-performing periods. To implement effectively:
- Analyze conversion data by day of week and hour of day
- Identify patterns in performance
- Increase bids during high-converting periods
- Decrease bids or pause ads during poor-performing times
This tactic works especially well for businesses with clear performance patterns, such as B2B services that convert best during business hours.
Competitor Targeting Techniques
While respecting trademark policies, you can strategically bid on competitor-related terms:
- Target users searching for competitor comparisons
- Bid on generic industry terms plus competitor names
- Create specific ad copy that addresses competitor comparisons
Always focus on your own value proposition rather than negative messaging about competitors.
Google Ads Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even experienced advertisers can fall into these common traps. Awareness is the first step to prevention.
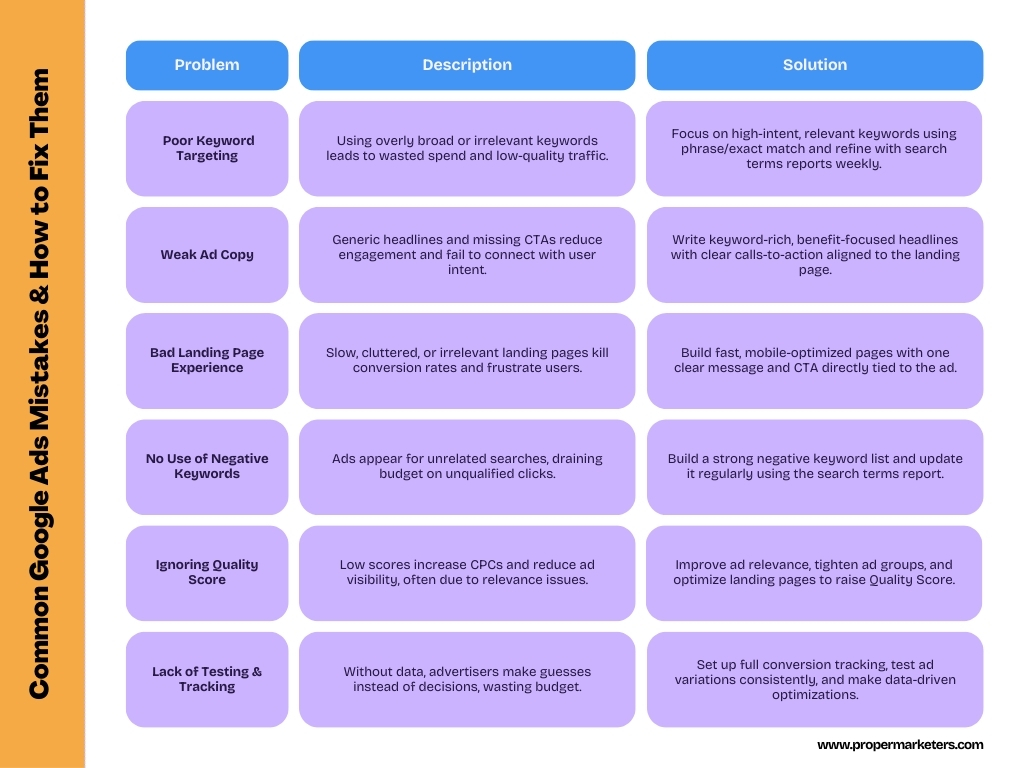
Poor Keyword Targeting
Mistakes:
- Using only broad match keywords
- Targeting irrelevant or overly general terms
- Selecting keywords based on volume rather than intent
- Ignoring search terms reports
Solutions:
- Use a mix of match types, emphasizing phrases and exact for core terms
- Focus on user intent rather than just volume
- Review search terms reports weekly to identify irrelevant matches
- Group keywords by theme in tightly focused ad groups
Weak Ad Copy or Irrelevant Offers
Mistakes:
- Generic headlines without unique selling propositions
- Failure to include keywords in ad copy
- Missing calls-to-action
- Disconnected messaging between ad and offer
Solutions:
- Include primary keywords in headlines
- Highlight specific benefits and unique advantages
- Use strong, clear calls-to-action
- Ensure ad messaging aligns perfectly with landing page offers
Neglecting Landing Page Experience
Mistakes:
- Sending all traffic to the homepage
- Slow loading pages or poor mobile experience
- Cluttered design with multiple competing calls-to-action
- Requiring too much information in forms
Solutions:
- Create substantial landing pages for each campaign or ad group
- Optimize for speed and mobile responsiveness
- Focus on a single, clear conversion path
- Keep forms short and only ask for essential information
Not Using Negative Keywords
Mistakes:
- Setting up campaigns without negative keywords
- Failing to review search terms reports regularly
- Using only exact match negative keywords
Solutions:
- Start with a foundational negative keyword list
- Review search terms reports weekly to identify irrelevant queries
- Use appropriate negative match types (broad, phrase, exact)
- Share negative keyword lists across relevant campaigns
Ignoring Quality Score
Mistakes:
- Focusing on geographic targeting to reach local customers
- Targeting specific niche keywords with less competition
- Creating highly relevant ads and landing pages
- Starting with a modest budget and scaling gradually
The main fact is to focus on quality and relevance rather than trying to compete for the most expensive keywords nationwide.
FAQs
How much of a budget do I need to start?
While there’s no minimum spending requirement for Google Search Ads, you’ll need enough money to gather meaningful data. Consider these guidelines:
- Testing phase: $500-1,000 per month minimum to test keywords and gather initial data
- Small local business: $1,000-2,500 per month can be effective for targeted local campaigns
- Mid-sized regional business: $2,500-10,000 per month allows for broader reach and testing
- Enterprise-level: $10,000+ per month for comprehensive campaigns across multiple markets
Rather than focusing solely on budget, calculate your target cost-per-acquisition based on your business economics. If acquiring a customer is worth $200 to your business, and your conversion rate is 5%, you could afford up to $10 per click ($200 × 5% = $10).
How long before I see results?
Google Search Ads can deliver impressions and clicks immediately after campaign launch, but meaningful performance data takes time:
- Traffic: Begins within minutes of campaign approval
- Initial conversion data: 1-2 weeks (depending on traffic volume)
- Statistically significant results: 2-4 weeks for most campaigns
- Campaign maturity: 3 months for full optimization and stable performance
Factors affecting timeline include:
- Industry competitiveness
- Budget size
- Campaign structure
- Seasonality
- Historical account performance
Be wary of making major changes without sufficient data, as this can reset the learning process.
Can I manage Google Ads myself or hire an agency?
This depends on several factors:
Self-management makes sense when:
- You have time to learn and manage campaigns (5+ hours weekly)
- Your ad spend is relatively small (under $2,500/month)
- You enjoy analytics and are comfortable with data
- Your campaigns are straightforward (single location, limited products)
Agency management is beneficial when:
- Your time is better spent on other aspects of your business
- Your monthly ad spend exceeds $2,500
- You need advanced strategies and optimization
- You require multi-location or complex campaigns
Many businesses start with self-management and transition to agency support as their campaigns grow in complexity and budget.
What is a good click-through rate?
Average CTRs vary significantly by industry, but these benchmarks provide general guidance:
- Search network average: 1.91%
- Top-performing search campaigns: 5-10%+
- Display network average: 0.35%
Industry-specific averages:
- Finance: 2.91%
- E-commerce: 1.66%
- Legal: 1.35%
- Health: 3.27%
- Technology: 2.09%
Rather than chasing industry averages, focus on improving your own CTR over time. Compare your performance to your historical data rather than arbitrary benchmarks.
What are negative keywords?
Negative keywords refer to preventive measures that block your ads from displaying for specific search terms, helping you:
- Avoid irrelevant traffic
- Reduce wasted spend
- Improve Quality Score
- Increase conversion rates
Common negative keyword categories include:
- Freebie seekers: “free,” “download,” “DIY”
- Informational queries: “how to,” “ways to,” “ideas”
- Job seekers: “jobs,” “careers,” “salary”
- Student queries: “essay,” “homework,” “assignment”
- Competitor brand terms (when not part of your strategy)
Regularly reviewing search terms reports and adding negative keywords is one of the most cost-effective optimization activities.
Final Thoughts
Google Search Ads represent one of the most resourceful digital marketing tools available to businesses today. By connecting with prospects at the exact moment they’re searching for solutions you provide, you can drive qualified traffic, generate more leads, and increase sales with measurable ROI.
The key to success waits in understanding the fundamentals outlined in this guide:
- Targeting the right keywords with appropriate match types
- Creating compelling ads that speak directly to user intent
- Building relevant, high-converting landing pages
- Implementing thorough tracking and optimization
- Continuously testing and refining your approach
Whether you’re just getting started with your first campaign or looking to improve existing performance, remember that Google Ads Search Campaigns are not a “set it and forget it” marketing channel. The most successful advertisers maintain a cycle of continuous improvement:
- Research and plan
- Implement and launch
- Measure and analyze
- Optimize and scale
- Repeat
Is your business ready to transform its online presence with targeted, high-performing Google Search Ads? Our team of certified Google Ads specialists at Proper Marketers can help you navigate the complexities of PPC Search Ads and develop customized strategies that deliver measurable results.
Don’t let another day go by while your competitors capture valuable search traffic. Start harnessing the power of Google Search Ads today! solely on bids while neglecting quality factors
- Not addressing low low-quality score keywords
- Creating large, loosely themed ad groups
Solutions:
- Regularly review the Quality Score at the keyword level
- Create tightly themed ad groups with highly relevant ads
- Optimize landing pages for relevance and user experience
- Pause or remove persistently low-quality keywords
Lack of Testing or Tracking
Mistakes:
- Running campaigns without conversion tracking
- Never testing ad variations
- Making changes without statistical significance
- Focusing on clicks rather than conversions
Solutions:
- Implement comprehensive conversion tracking before launching campaigns
- Always run at least two ad variations per ad group
- Wait for statistically significant data before making decisions
- Optimize for conversion metrics, not just clicks or impressions
Real-World Case Studies
Let’s examine how real businesses have leveraged Google Search Ads to achieve remarkable results.
Case Study 1: Local Service Business
Business: City Plumbing Services Challenge: Generating service calls for a small plumbing business in a competitive metro area Strategy:
- Geo-targeted campaigns focused on a 15-mile radius around the service area
- Implementation of call extensions and location extensions
- Creation of an emergency service ad group with higher bids
- Development of season-specific campaigns (winter pipe freezes, summer AC issues)
Results:
- 127% increase in phone call leads
- 43% reduction in cost-per-lead
- ROI of 720% (every $1 spent generated $7.20 in revenue)
- Business expanded service fleet from 3 to 7 trucks within 12 months
Key Takeaway: Precise geographic targeting combined with relevant seasonal messaging can dramatically improve local service business results.
Case Study 2: E-Commerce Retailer
Business: FashionForward (online clothing store) Challenge: Increasing sales while maintaining target ROAS of 400% Strategy:
- Implementation of Smart Shopping campaigns for best-selling products
- Creation of RLSA campaigns targeting past purchasers with higher bids
- Dynamic remarketing to cart abandoners with special offers
- Automated bidding using the Target ROAS strategy
Results:
- 82% increase in conversion volume
- Maintained 410% ROAS (exceeding target)
- 31% increase in average order value
- Shopping campaigns outperformed traditional search by 2.3x
Key Takeaway: Combining automated bidding with strategic remarketing creates powerful e-commerce results.
Case Study 3: B2B Software Company
Business: CloudAccounts (accounting software) Challenge: Generating qualified demo requests at under $200 CPA Strategy:
- In-depth keyword research focusing on problem-solving intent
- Creation of comprehensive comparison landing pages
- Implementation of lead form extensions
- Multi-step conversion tracking from demo request to sales-qualified lead
Results:
- Reduced cost-per-acquisition from $280 to $175
- Increased demo-to-sales conversion rate by 35%
- Expanded keyword coverage by 327%
- Achieved #1 average position for top industry terms
Key Takeaway: Understanding the buyer journey and tracking full-funnel metrics enables B2B advertisers to optimize for quality leads, not just quantity.
Free and Paid Tools to Supercharge Your Campaigns
The right tools can dramatically improve your Google Search Ads performance without requiring significantly more time investment.
Google Keyword Planner
This free tool within Google Ads helps:
- Discover new keyword concepts related to your business
- Get search volume data and trends
- See how competitive keywords are
- Estimate potential traffic and costs
Best for: Initial keyword research and campaign budget planning
Google Ads Performance Grader
Free tools like WordStream’s Ads Grader provide:
- Account performance benchmarking against similar advertisers
- Identification of wasted spend opportunities
- Quality Score analysis
- Suggestions for quick performance improvements
Best for: Quick audits and identifying major improvement opportunities
SEMrush, Ahrefs, SpyFu
These paid competitive intelligence tools offer:
- Competitor keyword analysis
- Ad copy and landing page insights
- Historical performance data
- Gap analysis between your campaigns and competitors’
Best for: Competitive research and identifying new opportunities
Landing Page Builders and A/B Testing Tools
Tools like Unbounce, Instapage, and Optimizely provide:
- Drag-and-drop landing page creation
- Built-in A/B testing capabilities
- Conversion rate optimization features
- Integration with Google Ads and analytics platforms
Best for: Creating and optimizing high-converting landing pages without developer resources
Call Tracking & Heatmaps
Advanced tracking tools like CallRail and Hotjar offer:
- Phone call recording and attribution
- Visitor behavior recording
- Click and scroll heatmaps
- User journey analysis
Best for: Understanding user behavior and optimizing for offline conversions
Your Google Ads Journey Starts Now
Picture this: You’re standing at the base of a mountain. At the summit waits a crowd of potential customers, eager to discover exactly what you offer. Google Ads is your sherpa for this climb—experienced, knowledgeable, and ready to guide you along the most efficient path to reach them.
Is your business still taking the long, winding trail when there’s a direct route available?
The businesses that thrive in today’s digital landscape aren’t actually the ones with the biggest budgets or the fanciest websites. They’re the ones who understand the power of being present at the exact moment someone needs them.
Google Ads transforms your business by:
- Making you visible when it matters most, like a lighthouse guiding ships safely to the harbor
- Converting interest into action — turning “just browsing” into “just purchased”
- Scaling with precision — allowing you to grow without wasting resources, like a gardener who knows exactly where to water
- Providing crystal-clear insights — shining a spotlight on what’s working and what isn’t
Time for an Honest Look
Take a moment (go ahead, we’ll wait) and ask yourself:
“If a potential customer searched for exactly what my business offers right now, would they find me or my competitor?”
If you hesitated even for a second, your current advertising strategy might be the equivalent of passing out business cards in a windstorm—perhaps well-intentioned, but hardly effective.
Ready for a deeper dive?
The Proper Marketers team offers complimentary 30-minute strategy sessions where we’ll analyze your current approach and identify three specific areas where Google Ads could create immediate impact for your business.
No pressure, no sales pitch—just expertise shared over a virtual coffee. Think of it as a test drive before committing to the journey.
The Ball’s in Your Court
As the digital world continues its evolution, standing still is the only guaranteed way to fall behind. Your competitors are likely already leveraging the power of Google Ads—crafting campaigns, analyzing data, and connecting with your shared audience pool.
But here’s the good news: It’s never too late to start, and you don’t have to navigate these waters alone.
The Proper Marketers team has helped businesses just like yours transform their digital presence from invisible to inevitable.
Whether you’re ready to launch your first campaign tomorrow or just curious about what’s possible, we’re here to help turn potential into profit.
Your future customers are searching. Will you be there when they find you?
Contact us today, and let’s write your Google Ads success story together.
